§ 98.463 Calculating GHG emissions.
(a) For each industrial waste landfill subject to the reporting requirements of this subpart, calculate annual modeled CH4 generation according to the applicable requirements in paragraphs (a)(1) through (a)(3) of this section. Apply Equation TT–1 of this section for each waste stream disposed of in the landfill and sum the CH4 generation rates for all waste streams disposed of in the landfill to calculate the total annual modeled CH4 generation rate for the landfill.
(1) Calculate annual modeled CH4 generation using Equation TT–1 of this section.
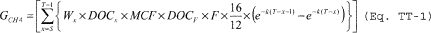
Where:
(2) Waste stream quantities. Determine annual waste quantities as specified in paragraphs (a)(2)(i) through (ii) of this section for each year starting with January 1, 1960 or the year the landfills first accepted waste if after January 1, 1960, up until the most recent reporting year. The choice of method for determining waste quantities will vary according to the availability of historical data. Beginning in the first emissions reporting year (2011 or later) and for each year thereafter, use the procedures in paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section to determine waste stream quantities. These procedures should also be used for any year prior to the first emissions reporting year for which the data are available. For other historical years, use paragraph (a)(2)(i) of this section, where waste disposal records are available, and use the procedures outlined in paragraph (a)(2)(ii) of this section when waste disposal records are unavailable, to determine waste stream quantities. Historical disposal quantities deposited (i.e., prior to the first year in which monitoring begins) should only be determined once, as part of the first annual report, and the same values should be used for all subsequent annual reports, supplemented by the next year's data on new waste disposal.