§ 98.153 Calculating GHG emissions.
(a) The mass of HFC–23 generated from each HCFC–22 production process shall be estimated by using one of two methods, as applicable:
(1) Where the mass flow of the combined stream of HFC–23 and another reaction product (e.g., HCl) is measured, multiply the weekly (or more frequent) HFC–23 concentration measurement (which may be the average of more frequent concentration measurements) by the weekly (or more frequent) mass flow of the combined stream of HFC–23 and the other product. To estimate annual HFC–23 production, sum the weekly (or more frequent) estimates of the quantities of HFC–23 produced over the year. This calculation is summarized in Equation O–1 of this section:
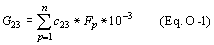
Where:
(2) Where the mass of only a reaction product other than HFC–23 (either HCFC–22 or HCl) is measured, multiply the ratio of the weekly (or more frequent) measurement of the HFC–23 concentration and the weekly (or more frequent) measurement of the other product concentration by the weekly (or more frequent) mass produced of the other product. To estimate annual HFC–23 production, sum the weekly (or more frequent) estimates of the quantities of HFC–23 produced over the year. This calculation is summarized in Equation O–2 of this section, assuming that the other product is HCFC–22. If the other product is HCl, HCl may be substituted for HCFC–22 in Equations O–2 and O–3 of this section.