§ 86.544-90 Calculations; exhaust emissions.
This section describes how to calculate exhaust emissions. Determine emission results for each pollutant to at least one more decimal place than the applicable standard. Apply the deterioration factor, then round the adjusted figure to the same number of decimal places as the emission standard. Compare the rounded emission levels to the emission standard for each emission data vehicle. In the case of NOX + HC standards, apply the deterioration factor to each pollutant and then add the results before rounding.
(a) Calculate a composite FTP emission result using the following equation:
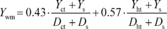
Where:
(b) The mass of each pollutant for each phase of both the cold-start test and the hot-start test is determined from the following:
(1) Hydrocarbon mass:
(2) Oxides of nitrogen mass:
(3) Carbon monoxide mass:
(4) Carbon dioxide mass:
(5) Methanol mass:
(6) Formaldehyde mass:
(7) Total hydrocarbon equivalent:
(8) Nitrous Oxide Mass:
(c) Meaning of symbols:
(1)
(i) HCmass = Hydrocarbon emissions, in grams per test phase.
(ii) DensityHC = Density of HC in exhaust gas.
(A) For gasoline-fuel; DensityHC = 576.8 g/m -carbon atom (16.33 g/ft -carbon atom), assuming an average carbon to hydrogen ratio of 1:1.85, at 20 °C (68 °F) and 101.3 kPa (760 mm Hg) pressure.
(B) For natural gas and liquefied petroleum gas-fuel; DensityHC = 41.57(12.011 + H/C(1.008)) g/m -carbon atom (1.1771(12.011 + H/C(1.008)) g/ft -carbon atom) where H/C is the hydrogen to carbon ratio of the hydrocarbon components of test fuel, at 20 °C (68 °F) and 101.3 kPa (760mm Hg) pressure.