§ 1066.605 Mass-based and molar-based exhaust emission calculations.
(a) Calculate your total mass of emissions over a test cycle as specified in paragraph (c) of this section or in 40 CFR part 1065, subpart G, as applicable.
(b) See the standard-setting part for composite emission calculations over multiple test intervals and the corresponding weighting factors.
(c) Perform the following sequence of preliminary calculations to correct recorded concentration measurements before calculating mass emissions in paragraphs (e) and (f) of this section:
(1) For vehicles above 14,000 pounds GVWR, correct all THC and CH4 concentrations for initial contamination as described in 40 CFR 1065.660(a), including continuous readings, sample bag readings, and dilution air background readings. This correction is optional for vehicles at or below 14,000 pounds GVWR.
(2) Correct all concentrations measured on a “dry” basis to a “wet” basis, including dilution air background concentrations.
(3) Calculate all NMHC and CH4 concentrations, including dilution air background concentrations, as described in 40 CFR 1065.660.
(4) For vehicles at or below 14,000 pounds GVWR, calculate HC concentrations, including dilution air background concentrations, as described in this section, and as described in § 1066.635 for NMOG. For emission testing of vehicles above 14,000 pounds GVWR, with fuels that contain 25% or more oxygenated compounds by volume, calculate THCE and NMHCE concentrations, including dilution air background concentrations, as described in 40 CFR part 1065, subpart I.
(5) Correct all gaseous concentrations for dilution air background as described in § 1066.610.
(6) Correct NOX emission values for intake-air humidity as described in § 1066.615.
(7) Correct all PM filter masses for sample media buoyancy as described in 40 CFR 1065.690.
(d) Calculate g/mile emission rates using the following equation unless the standard-setting part specifies otherwise:
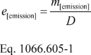
Where:
Example:
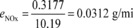
(e) Calculate the emission mass of each gaseous pollutant using the following equation:
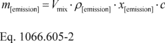
Where:
Example:
(f) Calculation of the emission mass of PM, mPM, is dependent on how many PM filters you use, as follows: