§ 63.10021 How do I demonstrate continuous compliance with the emission limitations, operating limits, and work practice standards?
(a) You must demonstrate continuous compliance with each emissions limit, operating limit, and work practice standard in Tables 1 through 4 to this subpart that applies to you, according to the monitoring specified in Tables 6 and 7 to this subpart and paragraphs (b) through (g) of this section.
(b) Except as otherwise provided in § 63.10020(c), if you use a CEMS to measure SO2, PM, HCl, HF, or Hg emissions, or using a sorbent trap monitoring system to measure Hg emissions, you must demonstrate continuous compliance by using all quality-assured hourly data recorded by the CEMS (or sorbent trap monitoring system) and the other required monitoring systems (e.g., flow rate, CO2, O2, or moisture systems) to calculate the arithmetic average emissions rate in units of the standard on a continuous 30-boiler operating day (or, if alternate emissions averaging is used for Hg, 90-boiler operating day) rolling average basis, updated at the end of each new boiler operating day. Use Equation 8 to determine the 30- (or, if applicable, 90-) boiler operating day rolling average.
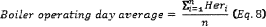
Where:
(c) If you use a PM CPMS data to measure compliance with an operating limit in Table 4 to this subpart, you must record the PM CPMS output data for all periods when the process is operating and the PM CPMS is not out-of-control. You must demonstrate continuous compliance by using all quality-assured hourly average data collected by the PM CPMS for all operating hours to calculate the arithmetic average operating parameter in units of the operating limit (e.g., milliamps, PM concentration, raw data signal) on a 30 operating day rolling average basis, updated at the end of each new boiler operating day. Use Equation 9 to determine the 30 boiler operating day average.
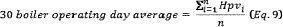
Where:
(1) For any exceedance of the 30-boiler operating day PM CPMS average value from the established operating parameter limit for an EGU subject to the emissions limits in Table 1 to this subpart, you must:
(i) Within 48 hours of the exceedance, visually inspect the air pollution control device (APCD);
(ii) If the inspection of the APCD identifies the cause of the exceedance, take corrective action as soon as possible, and return the PM CPMS measurement to within the established value; and
(iii) Within 45 days of the exceedance or at the time of the annual compliance test, whichever comes first, conduct a PM emissions compliance test to determine compliance with the PM emissions limit and to verify or re-establish the CPMS operating limit. You are not required to conduct any additional testing for any exceedances that occur between the time of the original exceedance and the PM emissions compliance test required under this paragraph.