Robin Singh (robinsingh002@yahoo.com) is the Compliance & Fraud Control Lead at Abu Dhabi Health Services Company in Abu Dhabi, UAE.
The financial system is meant to help the common man and businesses invest, save, manage, and diversify risks. This system is widespread with conflicts of interest and reckless practices, as seen in the recent subprime crisis.
In the end, the upper management of the banking industry is fairly invisible and unaccountable; however, it is the common man who faces the brunt of losing their savings. Every economic downturn needs a hero, and in came U.S. Senator Christopher J. Dodd and U.S. Representative Barney Frank to save the day and establish an ambitious overhaul of the financial system.
The incoming White House administration has indicated its intention to dismantle a key aspect of Barack Obama’s legacy: the Dodd-Frank Act. This article examines various facets of Dodd-Frank and what would happen if it was to be repealed.
1. What is Dodd-Frank?
Dodd-Frank, more appropriately referred to as the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the Act), is key legislation passed during the Obama administration in 2010. It was legislation that was devised to serve as a preventive measure against financial crisis scenarios similar to the one that occurred in 2008.
2. Why was it set up?
The provisions listed in the Act are spread across 2,000+ pages and are mainly focused on eliminating risk in the American financial system. The Act was enforced through the establishment of various agencies that were responsible for monitoring the multiple components that make up the Act. This also placed the same agencies in a position to monitor the American banking system as a whole.
One of the major agencies set up under the Dodd-Frank Act is the Financial Stability Oversight Council (FSOC), which primarily oversees major financial firms whose financial status and size can have a negative effect on the economy. FSOC identifies risks to the financial industry (e.g., banks, hedge funds, and insurance companies).
Another major agency is the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau (CFPB), which monitors predatory mortgage lending and educates consumers on mortgage terms and conditions with the objective of helping them make smarter decisions. In addition, the agency also oversees credit and debit cards, consumer lending, and consumer complaints. Other key components include:
-
Capital/liquidity requirements: New standards were established by the Federal Reserve concerning the type and amount of capital that financial institutions would have to protect from exposures.
-
The Volcker Rule: Named after Paul Volcker, who was the Federal Reserve chairman under President Jimmy Carter. The rule stops commercial banks from engaging in proprietary trading and speculative activities. To be more specific, hedge and private equity fund investments are more controlled.
-
The Securities and Exchange Commission and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission: The rule gives these agencies greater control over the regulation of over-the-counter derivatives trading.
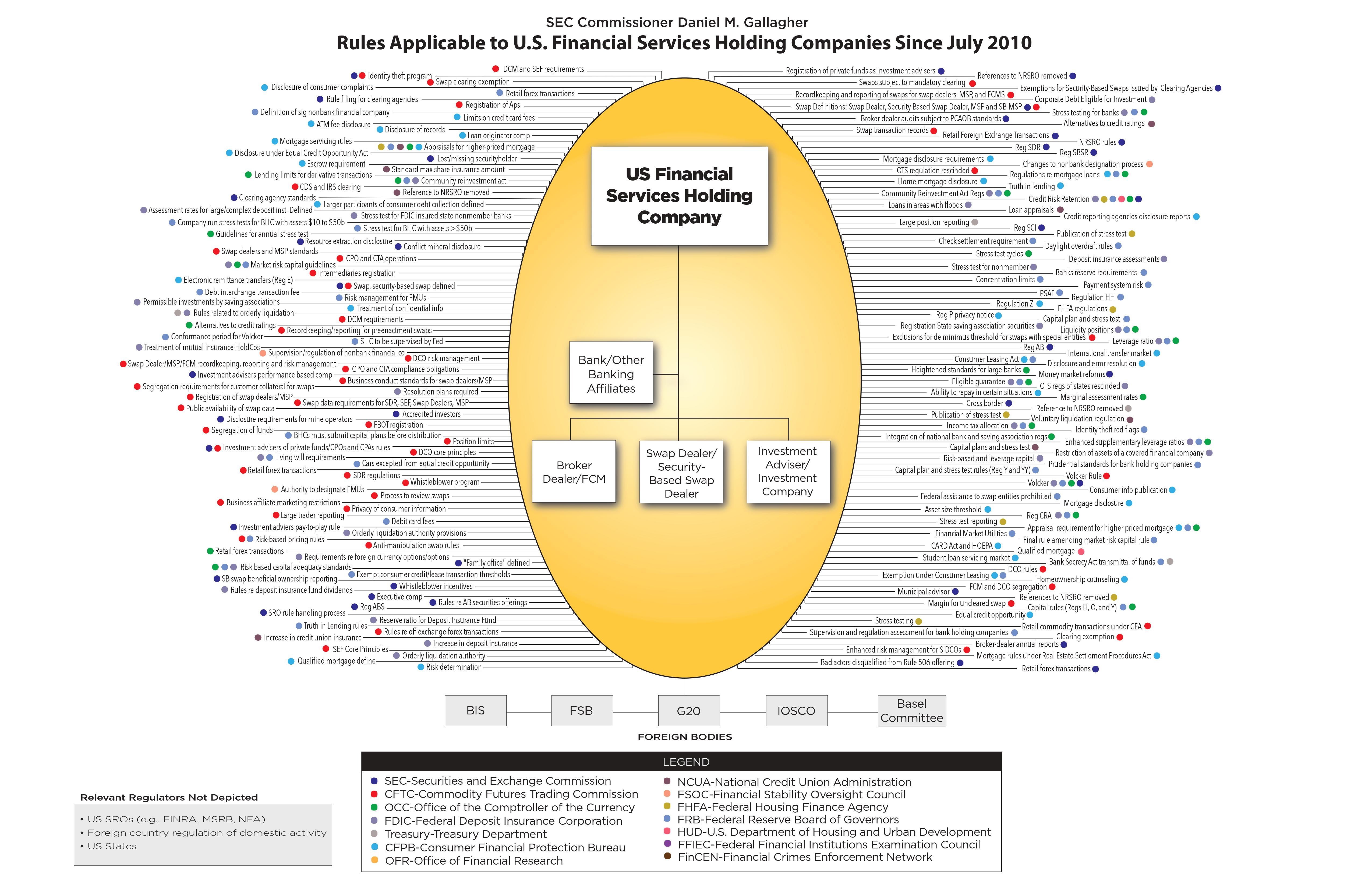
Dodd-Frank is so vast that corporations argue that regulatory burden has hampered their business growth. Figure 1, made by SEC Commissioner Daniel M. Gallagher, puts a high-level perspective on the reach of Dodd-Frank.