§ 98.253 Calculating GHG emissions.
(a) Calculate GHG emissions required to be reported in § 98.252(b) through (i) using the applicable methods in paragraphs (b) through (n) of this section.
(b) For flares, calculate GHG emissions according to the requirements in paragraphs (b)(1) through (3) of this section. All gas discharged through the flare stack must be included in the flare GHG emissions calculations with the exception of gas used for the flare pilots, which may be excluded.
(1) Calculate the CO2 emissions according to the applicable requirements in paragraphs (b)(1)(i) through (b)(1)(iii) of this section.
(i) Flow measurement. If you have a continuous flow monitor on the flare, you must use the measured flow rates when the monitor is operational and the flow rate is within the calibrated range of the measurement device to calculate the flare gas flow. If you do not have a continuous flow monitor on the flare and for periods when the monitor is not operational or the flow rate is outside the calibrated range of the measurement device, you must use engineering calculations, company records, or similar estimates of volumetric flare gas flow.
(ii) Heat value or carbon content measurement. If you have a continuous higher heating value monitor or gas composition monitor on the flare or if you monitor these parameters at least weekly, you must use the measured heat value or carbon content value in calculating the CO2 emissions from the flare using the applicable methods in paragraphs (b)(1)(ii)(A) and (b)(1)(ii)(B).
(A) If you monitor gas composition, calculate the CO2 emissions from the flare using either Equation Y–1a or Equation Y–1b of this section. If daily or more frequent measurement data are available, you must use daily values when using Equation Y–1a or Equation Y–1b of this section; otherwise, use weekly values.
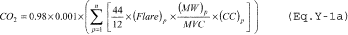
where:
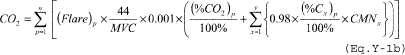
where:
(B) If you monitor heat content but do not monitor gas composition, calculate the CO2 emissions from the flare using Equation Y–2 of this section. If daily or more frequent measurement data are available, you must use daily values when using Equation Y–2 of this section; otherwise, use weekly values.
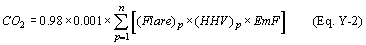
Where:
(iii) Alternative to heat value or carbon content measurements. If you do not measure the higher heating value or carbon content of the flare gas at least weekly, determine the quantity of gas discharged to the flare separately for periods of routine flare operation and for periods of start-up, shutdown, or malfunction, and calculate the CO2 emissions as specified in paragraphs (b)(1)(iii)(A) through (b)(1)(iii)(C) of this section.
(A) For periods of start-up, shutdown, or malfunction, use engineering calculations and process knowledge to estimate the carbon content of the flared gas for each start-up, shutdown, or malfunction event exceeding 500,000 scf/day.
(B) For periods of normal operation, use the average higher heating value measured for the fuel gas used as flare sweep or purge gas for the higher heating value of the flare gas. If higher heating value of the fuel gas is not measured, the higher heating value of the flare gas under normal operations may be estimated from historic data or engineering calculations.
(C) Calculate the CO2 emissions using Equation Y–3 of this section.
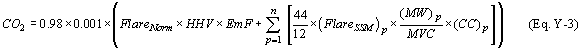
Where:
(2) Calculate CH4 using Equation Y–4 of this section.
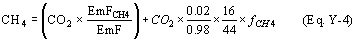
Where: